Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property WINP_SnippetShortcodePhp::$plugin is deprecated in /home3/miningio/public_html/S5SYSTEM/wp-content/plugins/insert-php/libs/factory/shortcodes/shortcode.class.php on line 95
Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property WINP_SnippetShortcodePhp::$plugin is deprecated in /home3/miningio/public_html/S5SYSTEM/wp-content/plugins/insert-php/libs/factory/shortcodes/shortcode.class.php on line 95
Here’s the sobering reality: across the Internet of Things (IoT), security has been overlooked. An amazing 1.51 billion IoT devices were breached in the first six months of 2021, an increase from 639 million in the same time period in 2020. With the anticipated number of connected devices worldwide predicted to reach ~29 billion by 2030, there is still a lot that needs to be done to ensure that these devices are protected from attacks.
IoT security is hard to predict
Consumers and device builders are increasingly aware of the importance of device security, but it can be challenging to know which devices are secure by design and which just haven’t been targeted yet. And for many device builders, security is an afterthought as they prioritize the features of the product or service itself when working towards a minimum viable product. Equally, security can sometimes be considered a necessary but un-exciting piece of the product development – the hoops you have to jump through. It can also be hard and therefore expensive to retro-fit security into an existing product.
Maybe these are some of the reasons we see insecure products released into the market. But it is worth remembering that the risk profile of a security incident is high and the impact can be extremely severe. If the worst was to happen, and a breach or hack occurs, you may well end up suffering company damaging impacts. Because of this high level of risk, the security of your data and device must be foundational, and must be built-in from the start.
Security needs to be considered as a necessary system component within your system architecture.

Common reactions to the challenges of IoT security
Security can come later
Before it became a household name, there were a series of security loopholes discovered with the Zoom client implementation across several platforms. Within the AV industry, there was a lot of comment, news articles, and concerns raised around the general security of the Zoom implementation. This, in turn, started to cause the kind of reputational damage that can be so damaging for a growing company.
Zoom’s response to these security concerns was pretty damn impressive. By pivoting to address the issues raised in a timely fashion, it managed to turn a problem into an opportunity – and to excel. Which is no mean feat. One can only imagine the sleepless nights for Zoom execs while these fixes were put in place – and I’m sure they would, in retrospect, have preferred to have had security as a core feature of the initial product, rather than an afterthought.
A breach will never happen to us
Several years ago, the connected security cameras from Hikvision were compromised through a weak password implementation and a back door / misuse of a cookie which resulted in devices being compromised. The Department of Homeland Security characterized the vulnerability as “remotely exploitable” with a “low skill level to exploit” – in other words, anyone with a computer and a little know-how could access another camera user’s footage.
Rather than this just being a security incident that was raised and publicized as so many are, actual users were targeted and the security of their devices was exploited. The hypothetical worst-case scenario of actual users and their data being hacked was a reality.
How costly can this become?
Last year, the well-documented Colonial Pipeline cyber attack took place and ransomware impacted computerized equipment managing the Texas based pipeline (a bit like a connected IoT device). This was only resolved when a 75 Bitcoin ransom (worth $4.4 million at the time) was paid.
Okay, so you have me worried
These examples are just some of the many security incidents, vulnerabilities, and design mistakes that affect products somewhere in the world every single day. As someone responsible for a connected device, the risk of a security incident should be enough to keep you awake at night. But the important thing is to learn and understand that similar things happen all the time.
Because unless you are aware of the risks as part of your product development, this too could happen to you. So – as an embedded software engineer, a device developer, a chief executive, or a product manager – what should you think about and look for to make sure that your device is one of the secure ones?

Key considerations for IoT security
1. Threat models
Firstly, you should start by considering threat models – what are you trying to protect, and who are you trying to protect? On one side, this boils down to protecting against accidental misuse and sloppy implementation (the Hikvision default password for example), through bad actors, rogue employees, untrusted manufacturing partners (the kind of things ISO 27001 helps protect against).
On the other side, it goes all the way through to hypothetical government-sponsored hacking, where silicon chips will be ‘de-capped’ and power supply injection used to read flash contents. The approach that you would consider necessary to protect against accidental misuse is somewhat different to that required to protect against state sponsored hacking.
2. Rules and regulations
The basics of IoT device security can be considered somewhat covered by legislation or certification and standards. For example, the most obvious ‘weak authentication’ – in general, a poor or default password – must be avoided, and is increasingly being included in new IoT legislation around the world (in California, Australia, and more recently, the UK). IoT legislation is attempting to banish the weak / default password approach, but this will still take time to adopt.
Standards – whether specific security standards (ARM PSA or SESIP, for example), or ISO implementations (ISO 27001, say) – can also help with some of the specific issues and people-based risks, putting in processes around which employees have access to which systems and the data within them. Many of these are essentially hoops you need to jump through, but if you can’t jump through the hoop, then your product is not ready for market.
3. The device itself
Microsoft has laid out one approach to device security in its paper on the seven properties of highly secure devices; here, it discusses seven properties that must be shared by all highly-secure network connected devices:
1. Hardware-based root-of-trust
2. Small trusted computing base
3. Defense in depth
4. Compartmentalization
5. Certificate-based authentication
6. Renewable security
7. Failure reporting
This forms a great basis for considering what your device needs to do in order to be secure. It is important to note Microsoft uses a custom silicon part to support these seven properties, but they can be achieved in a variety of ways and should all be considered necessary for IoT devices.
As well as these seven properties, there are some other things to consider for a secure device implementation, including:
8. Secure boot
9. Secure factory provisioning

Whatever you are thinking your threat model is, it is vital you control and manage the code running on your device. Because if you cannot trust the device is running the code you think it is, then you cannot trust anything.
To this end, a method of secure boot and secure factory provisioning is a must-have in order to trust the device and device code. The combination of these ensures your device is running your code.
If you can’t manufacture it securely, then it certainly isn’t secure. The need to get things ‘up-and-running’ quickly tends to lead to insecure implementations, as the many industrial cases built on Raspberry Pi testify. Raspberry Pi is great to get things moving, but it supports neither secure boot or factory provisioning. Secure-by-design, it is not. “A great hobbyist platform, but not suitable for commercial apps” – as Pen Test Partners told TechCrunch.
How to approach IoT security
The challenge can be that once you have committed to an approach, be it hardware or software, then switching or changing your development approach can be seen as both hard and costly. The inertia and the sunk-cost of the development combined with the pressure to get a product out-the-door often means that many developers and devices tend to stick with a relatively insecure approach.
To the end, it is crucial to ask how important a secure device implementation is. Is the approach properly secure? Are we happy with the risk level? What would happen if our devices were compromised? Crucially, it is important to decide whether the cost and risk of in-secure devices is worth it. Don’t be afraid to ask these questions, and to conclude security matters more. The earlier you do this, the better it will be. And remember: switching to a secure architecture isn’t as hard as it seems.
Interested in exploring Twilio Microvisor, and its secure architecture built for new generation of secure devices? Have a look at our whitepaper “Architecture and Design Considerations for Modern IoT Infrastructure”. Part I is written for a general technically inclined public audience, while Part II targets architects and engineers and goes into depth.
Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property WINP_SnippetShortcodePhp::$plugin is deprecated in /home3/miningio/public_html/S5SYSTEM/wp-content/plugins/insert-php/libs/factory/shortcodes/shortcode.class.php on line 95
Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property WINP_SnippetShortcodePhp::$plugin is deprecated in /home3/miningio/public_html/S5SYSTEM/wp-content/plugins/insert-php/libs/factory/shortcodes/shortcode.class.php on line 95
Smart Farming
Smart Farming is focused on the use of data acquired through various sources (historical, geographical, and instrumental) in the management of farm activities. Technologically advanced doesn’t essentially mean that it is a smart system. Smart agriculture technologies differentiate themselves through their ability to record the data and make sense of it. Smart farming employs hardware (IoT) and software (Software as a Service or SaaS) to capture the data and give actionable insights to manage all the operations on the farm, both pre-and post-harvest. The data is organized, accessible all the time, and full of data on every aspect of finance and field operations that can be monitored from anywhere in the world.
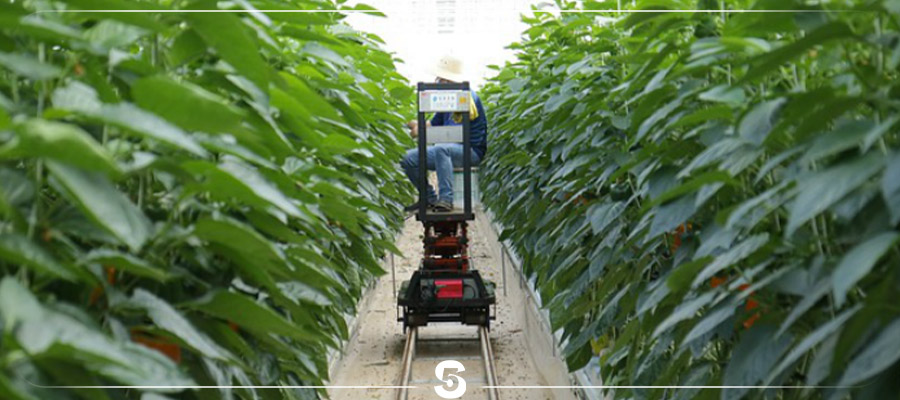

DIFFERENCES BETWEEN TRADITIONAL AND SMART FARMING
Implementing robotics in agriculture and other smart farming techniques brings in several benefits over conventional farming strategies. Some of these include exercising increased control over production processes, which in turn enhances cost management and reduces waste generation. In addition to this, smart farming, through the implementation of new technology in agriculture, makes it easier to trace anomalies in crop growth as well as livestock health.
Take a look at some of the key differences between traditional and smart farming practices.
TRADITIONAL FARMING
The same set of practices for crop cultivation, often unscientific, throughout the region
Imprecise application of fertilizers and pesticides throughout the field
Manual maintenance of all the field and finance data separately, leading to errors and data loss
Geo-tagging and zone detection are not possible
No reliable methods to predict the weather
Use of simple tools by farmers makes the process laborious and time-consuming

SMART FARMING
Each farm is analyzed to identify suitable crop varieties and input requirements for optimization and profitability
All farm data is centrally located on a digital platform
Early detection and application of inputs only in the affected region, saving costs
Uses satellite imagery to detect the different zones in farms
Reliable weather forecasts to maximize resource usage and minimize losses
Automation of tasks increases productivity and time- and cost-efficiency
Smart Farming for Food Safety
The Global Farming industry is facing many food safety challenges like non-standardized pest control, varying weather conditions, and also unpredictable contamination. These challenges are the sources of many diseases that cause great harm to human health. It also could negatively impact the credibility of food producers and manufacturers while exporting food products.
As the food supply chain is getting more and more complex, along with tough local and international food safety regulations, SaaS-based smart farming solutions, can transform the way the entire agri supply chain is managed.
Such solutions bring observability to agri businesses, and help them predict any anomalies and take corrective actions to prevent any food safety issue, in a cost-effective way.
NEW TECHNOLOGIES IN SMART AGRICULTURE: HOW DO AUTOMATION AND ROBOTICS HELP?
IoT in agriculture involves sensors, drones, and robots connected through the internet which function automatically and semi0automatically performing operations and gathering data aimed at increasing efficiency and predictability. With increasing demands and shortage of labor across the globe, agriculture automation and robots or commonly known as agribots are starting to gain attention among farmers. Crop production decreased by an estimated 213 crores approx ($3.1 billion) a year due to labor shortages in the USA alone. Recent advancements in sensors and AI technology that lets machines train on their surroundings have made agri-bots more notable.
The world is in the early stages of an ag-robotics revolution with most of the products still in R&D and trial phases.

Modern Agriculture Technologies
Semi-automatic robots with arms can detect weeds and spray pesticides on the affected plants, preventing extensive damage as well as reducing the overall pesticide costs. These robots can also be used in harvesting and lifting. Heavy farming vehicles can also be navigated from the comfort of homes through phone screens to perform tasks and GPS can track their positions at any time.
Drones equipped with sensors and cameras are used for imaging, mapping, and surveying the farms. They can be remotely controlled or they can fly automatically through agriculture software-controlled flight plans in their embedded systems, working in coordination with sensors and GPS. From the drone data, insights can be drawn regarding crop health, irrigation, spraying, planting, soil and field, plant counting and yield prediction, and much more.
IoT-based remote sensing utilizes sensors like weather stations placed on farms to gather data, which is then transmitted to analytical tools for analysis. They monitor the crops for changes in light, humidity, temperature, shape, and size. The data collected by sensors in terms of humidity, temperature, moisture precipitation, and dew detection helps in determining the weather pattern in farms so that cultivation is done for suitable crops. The analysis of the soil quality helps in determining the nutrient value and drier areas of farms, soil drainage capacity, or acidity, which allows for adjusting the amount of water needed for irrigation and the opt most beneficial type of cultivation.
Computer imaging involves the use of sensor cameras installed at different points on the farm or drones equipped with cameras. The images they capture undergo digital processing to derive meaningful insights from them. They are used for quality control, disease detection, irrigation monitoring, and sorting and grading the produce after harvest. Image processing using machine learning incorporates comparing images from a database with images of standing crops to determine the size, shape, color, and growth, therefore controlling the quality.
ROLE OF SAAS-BASED CLOUD SOFTWARE TECHNOLOGY IN SMART FARMING
Cloud-based software is used for the management of financial and field activities of farms. Prior to computers, farmers maintained data manually by keeping lengthy records on papers. This method was prone to human calculation errors. After the computer boom in the 1980s, it was not long before finance software such as Money Counts came to market. They intended to replace the spreadsheets to maintain the financial data.
The biggest challenge that farmers faced was the inability to manage field data. To address this, around the mid-2000s, satellite image use with tools like Raven Receiver for field zone tracking became widely used. Farmers had to implement and coordinate different tools to manage complete farm operations.
With constant improvements through the years, agritech SaaS has become an all-in-one tool for the management of all these activities and more in one place using a single tool. A good example would be Cropin. As a global agritech provider, we have worked with 200+ public and private sector organizations worldwide, utilizing deep learning, satellite monitoring, cloud computing, and other technological advancements to collect, analyze data, and manage all the activities from farm to fork with streamlined farm solutions.
]]>Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property WINP_SnippetShortcodePhp::$plugin is deprecated in /home3/miningio/public_html/S5SYSTEM/wp-content/plugins/insert-php/libs/factory/shortcodes/shortcode.class.php on line 95
Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property WINP_SnippetShortcodePhp::$plugin is deprecated in /home3/miningio/public_html/S5SYSTEM/wp-content/plugins/insert-php/libs/factory/shortcodes/shortcode.class.php on line 95
Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property WINP_SnippetShortcodePhp::$plugin is deprecated in /home3/miningio/public_html/S5SYSTEM/wp-content/plugins/insert-php/libs/factory/shortcodes/shortcode.class.php on line 95
IoT signifies a network of millions of devices communicating via the Internet. Mobile devices, wearables, and complex robots with people using them. These devices communicate over the Internet using hardware and software implants. Sensors enable these devices to interact with the environment through software applications.
Globally, the Internet of things (IoT) has played a key role in advancing technology. Businesses and organizations have used it to improve services and deliver better user experiences. You can even develop new technologies previously unimaginable.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and 5G networking rely on IoT. IoT devices execute more complex tasks and collect large amounts of data. By incorporating AI, it can improve automation and reduce errors. As of now, IoT has enjoyed a very successful year. IoT trends gained significant attention following the recent pandemic. This article discusses some of the IoT trends for 2022 impacting the industry.

Insights Into IoT Trends
Globally, IoT Analytics shows 17 billion connected machines. In the next few years, we can expect the usage of Internet of Things devices to reach 7 billion.
In 2022, the number of IoT devices will surpass laptops and smartphones. Internet of Things devices will number over 21 billion by 2025. IoT trends will continue to grow as a major force in the industry. IoT already has a $151 billion market value, which will skyrocket to $1.5 trillion by 2025.
A significant part of the growth will come from the consumer segment. Globally, internet users are on the rise, along with the popularity of smart devices. Consumers are adopting mobile apps to control their homes.
What To Watch For In IoT Trends 2022?
In this article, we will review some upcoming IoT trends for 2022. You can also see the potential of IoT to make our lives better or worse.
-
Cybersecurity Advancements
Currently, online IoT devices are greater than the world’s population. By the year 2022, this number will grow exponentially. In the recent COVID-19 pandemic, everyone had to stay indoors for extended periods. Since remote education and work have become the norm. Institutions and companies have invested heavily to expand their communication infrastructure. The result is an increase in the number of devices on the internet.
The proliferation of web-enabled devices has caused security to become a top priority. Due to the sudden boom in internet-connected devices, many users are unfamiliar with basic security practices. It is difficult for security agencies to monitor and secure many devices simultaneously. Security gaps aside, internet of things devices face a greater risk of cyberattacks.
Several companies are releasing up-to-date security updates and maintaining secure online practices. In 2022, the internet of things trend of improving cybersecurity will gain traction.
-
Incorporating IoT Applications Into The Healthcare Sector
Internet of things devices and applications came into widespread use in the healthcare sector even before the current pandemic. During the pandemic, the industry’s readiness to utilize new technologies frequently came to light. IoT adoption in the healthcare industry was ahead of the curve in 2021 without exaggerating. Use IoT to gather a large amount of useful data for the benefit of all.
Wearable health devices and blood oxygen monitors have significantly affected healthy and unhealthy lifestyles. Due to the improvement in healthcare IoT trends, 2022 will surely hit the success bell.

-
IoT Applications In The Business and Industrial Sectors
Among industrialists, IoT is also called the industrial internet. IoT has profound implications for product manufacturing and services. Logistics and factories use IoT infrastructure support for complete automation.
Robotics and Companies offer Internet-of-Thing (IoT) applications as a service. No wonder even the smaller companies will take advantage of the IoT trends in 2022. Companies can increase operational efficiency with the data-driven support of IoT. Augmented Reality and virtual reality have become increasingly popular in process simulation and equipment maintenance.
Internet of Things devices utilizes sensors to monitor machine performance. It can even forecast breakdowns and failures before they happen. Doing so makes replacing and repairing damaged equipment more efficient.
-
IoT and Growth of 5G Networks
A 5G network represents the foreseeable future of current mobile communications standards. 5G will improve speed, reliability, and data transfer speeds. Mobile networks will be much better than they are now. 5G will significantly improve IoT devices connectivity, with the backbone of the IoT. The internet of things devices that connect to the internet via 5G can transfer data quickly. In addition, IoT acts as a benchmark for the development of 5G. 5G developing firms will use the IoT conventions to expand the network capability.
-
The Wearable Technology Industry
The growth of technology has played an increasingly important role in our lives. IoT-enabled wearable devices will become more common. Many firms have already begun using smartwatches and VR headsets. Fitness and lifestyle organizations monitor their health with these devices. It will allow the tracking and monitoring of patients’ medical data in real-time.
-
IoT Data Management
Metadata management is critical to IoT solutions as they continuously collect millions of data points. In the face of an overwhelming amount of data, some IoT developers and users have not yet tapped into its full potential. IoT devices help tech companies to store and manage data in smarter ways. Every IoT device generates timestamped data. Increased analytics requirements have led to the boom of IoT data. Therefore, IoT platforms with specialized features have become more and more popular. By 2025, 60 billion connected devices will exist across the globe, with 95% connected to IoT platforms. Data storage is the first challenge. Integrating everything in real-time will be a challenge next year as IoT deployments grow rapidly.”

Are You Ready For The Future?
The traditional IT solutions no longer suffice in an increasingly connected world. IoT provides companies and consumers with a whole new world of possibilities. Data collection in real-time makes several processes more efficient and profitable. A new business model can even develop. A smarter home concept will benefit households with more users.
IoT will revolutionize industries like healthcare. Patients won’t have to visit a doctor whenever they feel ill. The use of smart sensors in transportation can reduce crashes. These sensors can predict routes and reduce travel costs drastically. A large part of this already exists in the top IoT trends for 2022. However, the fundamental paradigm shift is still to come.
-
How Will The Internet Of Things Develop In The Future?
IoT has limitless potential in the future. The increased mobility will lead to rapid advancements in the industrial internet. In a hyper-scale environment, improving network agility, AI integration, automation, orchestration, and security are important elements.
-
What Are The Latest Trends In IoT?
Here are six trends to watch in IoT:
- Cybersecurity Advancements
- Incorporating IoT Applications Into The Healthcare Sector
- IoT Applications In The Business and Industrial Sectors
- IoT and Growth of 5G Networks
- The Wearable Technology Industry
- IoT Data Management
-
What Will Make IoT Successful In The Coming Years?
Analytics of Things (AoT) and the Internet of Things (IoT) will contribute to faster and more precise decision-making. Depending on the sensors’ inputs received at the edge, it can automate or preprogram decision-making. IoT enables more efficient monitoring and process control whenever needed. Internet of things offers high-end security by integrating sensors in the backend systems.
]]>Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property WINP_SnippetShortcodePhp::$plugin is deprecated in /home3/miningio/public_html/S5SYSTEM/wp-content/plugins/insert-php/libs/factory/shortcodes/shortcode.class.php on line 95
Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property WINP_SnippetShortcodePhp::$plugin is deprecated in /home3/miningio/public_html/S5SYSTEM/wp-content/plugins/insert-php/libs/factory/shortcodes/shortcode.class.php on line 95
Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property WINP_SnippetShortcodePhp::$plugin is deprecated in /home3/miningio/public_html/S5SYSTEM/wp-content/plugins/insert-php/libs/factory/shortcodes/shortcode.class.php on line 95
Patient’s contacts with doctors were restricted, until the Internet of Things, to appointments, conferencing, and text messages. Doctors and hospitals were unable to keep track of their patient’s health and make rational decisions.
With the Internet of Things technologies, remote surveillance is now available in the healthcare industry. Which can keep patients safe and protected. At the same time enabling medical practitioners to provide better care while they are away.
With technology tools like video conferencing combined with real-time health statistics available to the medical practitioners, communication with doctors has become smoother and more effective resulting in increased trust and satisfaction for the patients.
Internet of Things (IoT) Applications for Healthcare:
The Internet of Things has the potential to fully improve healthcare for all the stakeholders in the ecosystem including but not limited to patients, medical practitioners, caretakers, hospitals, and insurance companies.

We can majorly classify the applications in the below major categories:
IoT for Patients
The Internet of Things has changed people’s lives, especially the lives of elderly patients, by allowing them to track and control their health conditions and issues. This has a huge impact on single persons and their families. When a person’s daily activities are moved, an alarm system sends warnings to family members and informed healthcare.
Wearables such as exercise bands and other wirelessly wired instruments such as blood pressure and heart rate control cuffs, glucometers. IoT devices provide patients with personalized care. These machines can be designed to remind you of things like calorie counting, exercising, appointments, blood pressure changes, and much more.
IoT for Medical Practitioners
Medical practitioners can keep better track of their patient’s well-being by using wearables and other IoT-enabled home surveillance devices. They will keep track of whether or not patients are sticking to their recovery schedules, as well as whether or not they need emergency medical attention. IoT allows healthcare providers to be more vigilant and compassionate in their interactions with patients.
IoT for Hospitals
The Internet of Things can be used in a wide variety of medical instruments, including wheelchair users, heart monitors, nebulizers, oxygen supplies, and other power storage devices.
For hospital patients, infection spread is a big concern. Hygiene management devices with IoT capabilities help in the prevention of infection in patients. Asset management, such as medication inventory tracking, and environmental control, such as measuring refrigerator temperatures and controlling humidity and temperature, is also made simpler with IoT devices.
IoT for Health Insurance Companies
With IoT-connected intelligent systems, health insurers have a variety of options. Data obtained by health tracking systems may be used by insurance providers for underwriting and claims management. They will be able to diagnose fraud allegations and classify underwriting opportunities using this information.

Benefits of IoT in Healthcare:
Cost savings
IoT provides for real-time patient tracking, reducing the amount of unwanted medical appointments, hospital stays, and re-admissions.
Enhances the capabilities of preventive medicine
Using IoT software, we can obtain a better understanding of the patient’s condition and react accordingly. Instead of waiting for symptoms to appear, doctors may use the information obtained to detect changes and easily resolve any concerns. For these reasons, the use of neural networks for data analytics in accordance with large amounts of IoT data is acceptable.
Increased hospital staff versatility and alertness
This is one of the most important IoT benefits of healthcare that would benefit frontline workers. In the case of a pandemic influenza epidemic, a growing number of patients may need urgent medical assistance.
Doctors are being forced to take on positions that they are not qualified to manage. They need software that helps them to track thousands, of patients in real-time. They can receive immediate alerts when critical changes in patient parameters occur, quickly locate patients. Who require assistance, and direct assistance as soon as possible using IoT tracking systems.

Drug and Medical Equipment Management
Healthcare providers can use IoT and medical software for medical practitioners to remotely verify whether a patient has taken their medications and if they haven’t, the therapist can call and inform the patient, or even simplify the procedure.
Reducing Errors
Usually, results turn wrong, or the doctor works an incorrect test or conclusion. In medicine, the social aspect may have important consequences. This is generally avoided with IoT due to checks and balances. The device can have the best performance in terms of diagnostic accuracy.
Patient data collection is sped up
Doctors usually spend hours analyzing various types of data. With the help of IoT, it will take a few minutes. Furthermore, the IoT when paired with AI and machine learning, will have care solutions.
Because of its diverse range of applications in various sectors, the growth of IoT is inspiring for everybody. It has a lot of functions in healthcare.
- Reducing emergency room wait time
- Tracking patients, staff, and inventory
- Enhancing drug management
- Ensuring availability of critical hardware
IoT has since launched a range of wearables and accessories that have made patient’s lives easier. The following are the devices:
- Hearables
- Ingestible sensors
- Moodables
- Computer vision technology
- Healthcare charting

Future Effect of IoT in Healthcare:
The popularity of smartphones and wireless networking, as well as the high costs of sensor technology, are two major factors behind IoT’s large projected growth in the healthcare industry.
With modern Internet of Things technologies helping develop healthcare, the IoT healthcare industry sector is rapidly solving potential technological implementation challenges and constantly upgrading the digital healthcare system by taking the benefits of innovative developments to doctors and patients.
Around 2015 and 2020, the healthcare Internet of Things (IoT) market will expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 37.6 percent. If there is one thing that is clear, it is that the Internet of Things has changed healthcare in a multitude of areas over the last few years and will continue to do so in the future.
In healthcare, what role does the Internet of Things play?
Let’s explore an IoT healthcare workflow example:
- A patient’s data is collected by a sensor.
- With the help of AI-driven algorithms like machine language (ML) , an IoT device sends the collected data.
- The computer must decide whether to take action or transfer the data to the cloud.
- On the basis of the data provided by the IoT system, doctors, health professionals. And even robots will make actionable and intelligent decisions.
Conclusion
In recent times, the future of IoT in healthcare seems bright. The current state of the market, as a result of the pandemic. Has once again shown the importance of using technologies like IoT, big data, and AI to improve. The safety and security of healthcare.
The Internet of Things is changing the way healthcare services are delivered. These innovations enhance the product by combining small improvements to have a greater result.
]]>
Internet of Things (IoT) is quickly gaining popularity in all spheres of life, healthcare systems in particular. In the nutshell, the technology allows multiple connected devices to collect and share information with each other.
What does this mean for healthcare?
In fact, the applications are so diverse that you would not probably even believe the examples are taken from real life. Here are just a few:
- Symptom-tracking apps that send updates on responses to cancer treatment to the physician and, thus, allow to avoid hospitalization;
- Connected hospital equipment that notifies doctors of its current location, informs the hospital management of the replacement needs and monitors staff performance
- Remote temperature monitoring ensuring the correct transportation and storage of vaccines;
- Healthcare IT solutions that remind patients to refill medication and digestible sensors that trigger a notification if the medication has not been taken in time;
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM) and smart insulin pens (record and recommend on the time and the amount of insulin dose injection) that come to the rescue to diabetics;
- Smart inhalers connected to an app that help people with asthma and pulmonary disease understand what causes the symptoms and predict allergens.
Given such examples, the Internet of Things (IoT) is seen as a way of living a smarter and safer life, and its application is highly encouraged in medical establishments. However, digital transformation in healthcare is not without threats. It is important to weigh all the advantages and disadvantages of implementing IoT systems in healthcare to be able to plan for ways to maximize the pros while mitigating the cons.

Major Advantages of IoT in Healthcare
The overall importance of healthcare software solutions is difficult to overestimate as technology promises to make healthcare services more effective and alleviate the burden placed on healthcare providers. This is critical in the context of the aging population and the increase in the number of chronic diseases.
The main advantages of IoT implementation in healthcare comprise:
1. Remote monitoring
Realtime remote monitoring via connected IoT devices and smart alerts allow to diagnose illnesses, treat diseases and save lives in case of a medical emergency
2. Prevention
Smart sensors may analyze health conditions, lifestyle choices and the environment and recommend preventative measures, which will reduce the occurrence of diseases and acute states
3. Reduction of healthcare costs
IoT reduces costly visits to doctors and hospital admissions and makes testing more affordable too
4. Medical data accessibility
Accessibility of electronic medical records allow patients to receive quality care and help healthcare providers to make the right medical decisions and prevent complications
5. Improved treatment management
IoT helps to track the administration of drugs and the response to the treatment and reduce medical error
6. Improved healthcare management
Using IoT, healthcare authority can get valuable information about equipment and staff effectiveness and use it to suggest innovations
7. Research
Since IoT devices are able to collect and analyze a massive amount of data, they have a high potential for medical research purposes
IoT in Healthcare: Challenges and Threats
Although the Internet of Things can be of great benefit to healthcare, there are still major challenges to address before full-scale implementation. The threats and disadvantages of using connected devices in healthcare are as follows:
1. Security and privacy
Security and privacy remain a major concern deterring users from using IoT technology for medical purposes, as healthcare monitoring solutions have the potential to be breached or hacked. The leak of sensitive information about the patient’s health and location and meddling with sensor data can have grave consequences, which would counter the benefits of IoT
2. Risk of failure
Failure or bugs in the hardware or even power failure can impact the performance of sensors and connected equipment, placing healthcare operations at risk. In addition, skipping a scheduled software update may be even more hazardous than skipping a doctor checkup
3. Integration
There is no consensus regarding IoT protocols and standards, so devices produced by different manufacturers may not work well together. The lack of uniformity prevents full-scale integration of IoT and, thus, limits its potential effectiveness
4. Cost
While IoT promises to reduce the cost of healthcare in the long-term, the cost of its implementation in hospitals and staff training is quite high
The Future of IoT in Healthcare
According to the Business Insider report, the market for IoT healthcare technology will rise to $400 billion by 2022. Such growth will be due to the increasing demand, the improvement of 5G connection and IoT technology, and the growing acceptance of healthcare IT software. The plans of tech giants like Apple, Google, and Samsung to invest in bridging the gap between fitness tracking apps and actual medical care are sure to contribute to the process too.
Despite the downsides, further digital transformation in healthcare is inevitable, and the concept of IoT will continue to capture and change the landscape of healthcare services. Thus, it seems to be high time to look beyond the challenges and embark on the journey to connected healthcare devices.
]]>The usage of the Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare (the industry, personal healthcare and healthcare payment applications) has sharply increased across various specific Internet of Things use cases. At the same time we see how other healthcare IoT use cases are picking up speed and the connected healthcare reality is accelerating, even if hurdles remain.
Thus far, most IoT initiatives in healthcare revolved around the improvement of care as such with remote monitoring and telemonitoring as main applications in the broader scope of telemedicine. A second area where many initiatives exist is tracking, monitoring and maintenance of assets, using IoT and RFID. This is done on the level of medical devices and healthcare assets, the people level and the non-medical asset level (e.g. hospital building assets).
However, these deployments and use cases are just the beginning and, at the same time, are far from omnipresent. More advanced and integrated approaches within the scope of the digital transformation of healthcare are starting to be used with regards to health data aspects where IoT plays an increasing role, as it does in specific applications such as smart pills, smart home care systems, personal healthcare, robotics and Real-Time Health Systems (RTHS).

Towards a more integrated and mature IoT-enabled eHealth reality
Within the overall connected healthcare and eHealth picture, more integrated approaches and benefits are sought with a role for the so-called Internet of Healthcare Things (IoHT) or Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). The period from 2017 until 2022 will be important in this transition, with several changes before 2020.
From 2017 until 2022, growth in IoT healthcare applications is indeed poised to accelerate as the Internet of Things is a key component in the digital transformation of the healthcare industry and various stakeholders are stepping up their efforts.
Moreover, there is an increasing consciousness and engagement of consumers with regards to their health, demand for remote and home possibilities keeps growing, various healthcare ecosystem players come up with novel approaches and partnerships; and healthcare expenditure reduction remains a main goal, along with better quality care. A more integrated and IoT-enabled eHealth approach proves essential in all these areas.
Some regions, such as the US, are leading in healthcare IoT and in leveraging health-related data from IoT devices. According to the 2017 Thales Data Threat Report, healthcare edition, which we covered in an article on healthcare and cybersecurity, already 30 percent of healthcare organizations use IoT for sensitive data.
March 2017 research from Aruba Networks (more below) found that by 2019, 87 percent of healthcare organizations will have adopted Internet of Things technology and 76 percent believe it will transform the healthcare industry.
More data and evolutions in the mentioned articles. Let’s now look at some key aspects and use cases within the broader scope of the Internet of Things in the healthcare sector.
The vast landscape of healthcare stakeholders and IoT possibilities
We once started listing all the applications, examples and use cases regarding the usage of the Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare. We had to stop.
The reason: healthcare is such a vast ecosystem and once you also start including personal healthcare, the pharmaceutical industry, healthcare insurance, RTHS, healthcare building facilities, robotics, biosensors, smart beds, smart pills, anything remote and the various healthcare specializations, activities and even (treatments of) diseases, that list of Internet of Things applications in healthcare quickly becomes endless.
In the scope of this article we don’t focus on pharma nor on how IoT (and AI) helps in the treatment of specific diseases or the evolutions with regards to specific areas such as bionic limbs and others.
The mentioned vastness goes both for the IoT use cases and the real-life applications of the Internet of Things in the healthcare industry. Still, as said some use cases clearly stick out if we look at applications and evolutions on the side of healthcare providers and healthcare payers.
Acceleration in all IoT use case and applications in healthcare ahead
Two things are for sure: 1) the main IoT use case in healthcare for now is (remote) health monitoring, certainly from an IoT spending perspective and 2) the Internet of Things will soon be pretty ubiquitous in healthcare and health-related activities and processes on various levels.
Moreover, we see that devices and IoT applications, which traditionally fit more in a consumer context (e.g. personal health trackers) get an increasing place in the relationship between consumer/patient and healthcare providers and payers. Patient engagement and consumer consciousness play an important role here and in the relationship with healthcare payers also incentives and Premiums do (compare with the use of telematics in in insurance).
Outside of this scope there is major growth ahead in a more Industrial Internet of Things context, whereby healthcare providers, such as hospitals, leverage IoT, in combination with applications and technologies in the field of robotics, artificial intelligence and Big Data.
The second focus area of IoT applications we mentioned in the introduction (monitoring, tracking, maintenance and so forth) is certainly also going to keep growing; albeit at difference paces, depending on the hospital, country and so on. Some will start with tracking anything from medical equipment and patients to hospital building assets and beds, others will move to the next stages.

Internet of Things in the context of healthcare transformation and the challenges of information-driven healthcare
Remote health monitoring – and various other IoT use cases in healthcare need to be seen in the context of the main challenges in healthcare and the areas with a clear benefit and/or purpose/possibility of innovation.
The developments regarding the Internet of Things in healthcare also need to be seen in the context of the digital transformation of the various healthcare segments. IoT, from an enablement perspective, is a cornerstone of the digital transformation of healthcare until at least the next decade.
The Internet of Things and healthcare information systems
In a health data context de facto quite some data from medical devices and monitoring systems ultimately end up in Electronic Healthcare Records (EHR) Systems or in specific applications which are connected with them and send the data to labs, doctors, nurses and other parties involved.
As health-related data is collected and increasingly is available in real-time, it gets integrated with electronic healthcare records (EHR).
EHR systems are far from omnipresent and most have not been designed with the Internet of Things, RFID and real-time data in mind; they have been designed, if all is well, to make healthcare faster, more patient-centric, more affordable and better from the perspective of the patient’s health and the work of healthcare professionals, based on rather static data.
These outcomes are also essential in many IoT use cases in healthcare, yet they are not always achieved. Moreover, there are so many approaches to the digitization of healthcare records that in practice an Internet of Things deployment needs to take into account these differences if it is related with an individual patient.
Not all health data from connected devices ultimately lands in the EHR/EMR environment. There are plenty of other information systems and systems of insight, depending on type of data, device, scope and purpose. Moreover, there is a shift towards Real-Time Health Systems (RTHS), which go beyond EHR and include awareness and real-time data capabilities in an IoT and connected/wearable device perspective. EHR systems are part of the broader context and processes within this RTHS systems approach.
According to Mind Commerce research “RTHS will be a key area for IoT in healthcare as Big Data Analytics tools and processes are utilized to evaluate both dynamic and static data for predictive analytics as part of comprehensive healthcare systems improvement programs”.
Healthcare data: working with purpose and security in mind
A second challenge has to do with the data. Healthcare information is very personal and the selection of the required data needs to happen with the outcomes in mind.
It’s the data that makes sense to improve the lives of patients and the organization of healthcare across its various aspects such as the ability for doctors, specialists, nurses and staff to make better decisions faster.
Moreover, security and privacy by design need to be part of any IoT use case, project or deployment. Leveraging the IoT and data aims to improve and reduce errors and costs. Making sure it doesn’t get exposed or used for the wrong reasons is key.
As mentioned in other articles, personal healthcare data needs to be treated differently from a security and compliance perspective.
Special attention for personal data in healthcare IoT projects needed
Various regulations across the globe drive the compliance agenda, yet healthcare data security needs to go beyond compliance.
At the same time, healthcare organizations need to pay more attention to compliance as well, certainly in regions where stricter regulations are being put into place such as the EU GDPR where personal health data, as well as genetic and other medical and biological data, get special attention and are seen as very sensitive.
It is clear that any IoT project which involves personal health data, needs to take these rules and the lawfulness, intent, and diffusion stipulations, to name a few, into account. As a matter of fact, any IoT project should have security and privacy by design in mind where it concerns personal data.
However, the positions with regards to the protection and leverage of health data is, to put it mildly, very different if you start comparing initiatives and regulations across the globe.
The Internet of Things in healthcare: use cases and major evolutions
Taking all the above into account let’s take a look at the major use cases today and, next, the rapidly emerging use cases in the near future.
Remote health monitoring and telehealth
As mentioned, remote health monitoring for now is the major IoT use case in the Internet of Healthcare Things (IoHT). In other words: today’s major use case from an IoT spending perspective is outside the setting of a hospital or other healthcare facility.
There is a general shift of care in hospitals or emergency care environments to private environments such as the patient’s home, whenever that becomes possible.
It’s a matter of costs, it’s a matter of getting the patient back to his ‘normal environment’ and it’s one way to reduce the workload of healthcare workers who in many countries and many periods simply can’t cope. In some countries the lack of funding and, as a result, shortage of healthcare workers, specifically in and after seasons where more diseases strike, is a recurring yearly disaster. Remote health monitoring, which is obviously very possible thanks to the Internet of Things, also partially helps solve the rise of chronic diseases, among others due to an aging population (but not just that). Remote health monitoring is also ideal when patients live in remote areas.
There is a broad range of (specialized) wearables and biosensors, along with other medical devices, available today that enables remote health monitoring.
Remote health monitoring also offers healthcare stakeholders the possibility to detect patterns, leveraging the data coming from these wearables and other devices. This enables new insights and visualizations of patterns as the combination of (big) data, analytics, IoT and so forth tends to do.
It is one reason why the skillsets of, for example, hospital staff, are changing. In practice, as budgets in healthcare are restricting, this could lead to concerns from a human care perspective.
The connected and smart hospital – a broad range of applications
Speaking about hospitals, there is a set of IoT use cases which brings us back from the remote aspect to hospitals and other healthcare facilities.

From maintenance of healthcare equipment to smart beds
So, this is not one specific IoT use case but rather a range which we could call the smart or connected hospital.
On the most essential level, which we touched upon earlier, we are speaking about RFID and IoT-enabled devices, IoT-enabled “assets” and rather traditional general IoT use cases which are really cross-industry such as (predictive) maintenance of hospital assets, connected healthcare devices and the tracking of healthcare devices (and people).
It isn’t really a surprise that this is an ongoing evolution, which on other levels, also includes phenomena such as smart beds, the aggregation and real-time availability of data from healthcare devices and assets regarding specific patients, and the advent of robots in a hospital environment for routine tasks.
Applications in the asset- and information-intensive hospital
After all, the hospital is an asset- and device-intensive environment with medical equipment and a wide range of objects that can be connected and monitored in order to achieve tangible benefits.
In such asset-intensive environments which at the same time are extremely information-intensive, ample possibilities and potential outcomes emerge when leveraging IoT and related sets of technologies.
In a cross-industry perspective we can certainly also mention smart buildings and facility management here. If there is one place where the various building parameters (think about temperature, humidity, air regulation, specific environmental controls, security and so forth) need to be optimal, it for sure is the hospital.
According to the previously mentioned 2017 research by Aruba Networks on the state of IoT in healthcare (and more), the main IoT use case in healthcare organizations is monitoring and maintenance (73 percent of respondents), followed by remote operation and control (50 percent of respondents). Connecting IoT devices is indeed an important goal to reap the benefits from IoT with 67 percent of respondents planning to connect their IoT devices using Wi-Fi.
The major perceived benefits, finally, are increased innovation (80 percent), visibility across the organization (76 percent) and, as always but in healthcare organization even more important, cost savings.
]]>Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property WINP_SnippetShortcodePhp::$plugin is deprecated in /home3/miningio/public_html/S5SYSTEM/wp-content/plugins/insert-php/libs/factory/shortcodes/shortcode.class.php on line 95

Thousands of errors occur in hospitals every day. Catching them, or even tracking them, is frustratingly ad-hoc. However, connectivity and intelligent distributed medical systems are set to dramatically improve the situation. This is the revolution that the Internet of Things (IoT) promises for patient safety. Stan Schneider, CEO Real-Time Innovations (RTI), explains.
Hospital error is the sixth leading cause of preventable death in the US. It kills over 50,000 people every year in the US alone, and likely ten times more worldwide. It harms one in seven of those hospitalised and it frustrates doctors and nurses every day.
This problem is not new. Thirty years ago, the last major change in healthcare system technology changed hospital care through a simple realisation – monitoring patients improves outcomes. That epiphany spawned the dozens of devices that populate every hospital room, like pulse oximeters, multi-parameter monitors, electrocardiogram (ECG) monitors and more. Over the ensuing years, technology and intelligent algorithms improved many other medical devices, from infusion pumps (IV drug delivery) to ventilators. Healthcare is much better today because of these advances. But errors persist. Why?
Today, these devices all operate independently. There’s no way to combine the information from multiple devices and intelligently understand patient status. Devices therefore issue many nuisance alarms. Fatigued healthcare staff members silence the alarms, misconfiguration goes unnoticed and dangerous conditions go unaddressed. And as a result, people die.
Hazards during heart surgery
For instance, there are 14 infusion pumps, each administers a different drug to a single patient. As seen in Figure 1 (above), the pumps are completely independent from each other and the other devices and monitors. This picture is of an intensive care unit (ICU) – an operating room (OR) needs a similar array. During heart surgery, for instance, drugs sedate the patient, stop the heart, start the heart and more. Each drug needs its own delivery device, and there are many more devices, including monitors and ventilators. During surgery, a trained anesthesiologist orchestrates delivery and monitors status. The team has their hands full.
After surgery, the patient must transfer to the ICU. This is a key risk moment. The drug delivery and monitor constellation must be copied from the operating room to the ICU. Today, the OR nurse calls the ICU on the phone and reads the prescription from a piece of paper. The ICU staff must then scramble to find and configure the correct equipment. The opportunity for small slips in transcription, coupled with the time criticality of the change, is fertile ground for a deadly error.
Consider if instead these systems could work together in real time. The OR devices, working with a smart algorithm processor, could communicate the exact drug combinations to the Electronic Medical Record (EMR). The ICU system would check this data against its configuration. Paper and manual configuration produce far too many errors – this connected system eliminates dozens of opportunities for mistakes.
Connectivity for post operation
Once in post op, the danger is not over. Many patients use patient controlled analgesia (PCA) systems (see Figure 2). The PCA system allows the patient to self-administer doses of painkiller medication by pressing a button. The idea is that a patient with sufficient pain medication will not press the button, and therefore be safe from overdose. PCA is efficient and successful, and millions of patients use it every year. Still, PCA overdose kills one to three patients every day in the US. This seemingly simple system suffers from visitor interference, unexpected patient conditions, and especially false alarm fatigue.
Connectivity can also help here. For instance, low oximeter readings cause many alarms. They are only likely to be real problems if accompanied by a low respiratory rate. A smart alarm that checks both oxygen (SPO2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) levels would eliminate many distracting false alarms. An infusion pump that stopped administering drugs in this condition could save many lives. These are only a few examples. The list of procedures and treatments that suffer from unintended consequences is long. Today’s system of advanced devices that cannot work together is rife with opportunity for error. The common weakness? Each device is independent. Readings from one device go unverified, causing far too many false alarms. Conditions easily detected by comparing multiple readings go unnoticed. Actions that can save lives require clinical staff interpretation and intervention.
Data Distribution Service (DDS) standard
The leading effort to build such a connected system is the Integrated Clinical Environment (ICE) standard, ASTM F2761. ICE combines standards, it takes the data definitions and nomenclature from the IEEE 11073 (x73) standard for health informatics. ICE data communications leverage the Data Distribution Service (DDS) standard. ICE then defines control, datalogging and supervisory functionality to create a connected, intelligent substrate for smart clinical connected systems. For instance, the supervisor combines oximeter and respirator readings to reduce false alarms and stop drug infusion to prevent overdose. The DDS DataBus connects all the components with appropriate real time reliable delivery (Figure 3).
DDS is an IoT protocol from the Object Management Group (OMG). While there are several IoT protocols, most focus on delivering device data to the cloud. The DDS DataBus architecture understands and enforces correct interaction between participating devices. DDS focuses on the real-time data distribution and control problem. It can also integrate with the cloud, or connect to other protocols to form a complete connected system. Its unique capabilities fit the medical device connectivity problem well.

Clinical challenges
While the above examples and scenarios are simple, networking medical devices in a clinical environment is quite challenging. Information flow mixes slow data updates with fast waveforms. Delivery timing control is critical. Integration with data from the EMR must provide patient parameters such as allergies and diagnoses. Appropriate monitor readings and treatment history must also be written to the EMR. Large hospitals must match data streams to patients, even as physical location and network transports change during transfers between rooms. Devices from many different manufacturers must be coordinated.
ICE leverages DDS to address these clinical challenges. DDS models the complex array of variables as a simple global data space, easing device integration. Within the data space, the data-centric model elevates programmes to exchange the data itself instead of primitive messages. It can sift through thousands of beds and hundreds of thousands of devices to find the right patient, despite moves. DDS is fast and operates in real time. It easily handles heart waveforms, image data and time critical emergency alerts.
Dr. Julian Goldman leads ICE. He is a practicing anesthesiologist with an appointment at Harvard Medical School, and he is also the director of Bioengineering at the Partners hospital chain. His Medical Device Plug-n-Play (MDPnP) project at the Center for Integration of Medicine and Innovative Technology (CIMIT) connects dozens of medical devices together. MDPnP offers a free open source reference platform for ICE. There are also commercial implementations, including one from a company called DocBox. The CIMIT lab uses these to prototype several realistic scenarios, including the PCA and OR-to-ICU transfer scenarios described here. It demonstrates what is possible with the IoT.
New connected implementation
Hospital error today is a critical healthcare problem. Fortunately, the industry is on the verge of a completely new connected implementation. Smart, connected systems can analyse patient conditions from many different perspectives. They can aid intelligent clinical decisions, in real time. These innovations will save lives. This technology is only one benefit of the IoT future, which will connect many billions of devices together into intelligent systems. It will change every industry, every job and every life. And one of the first applications will extend those lives.
]]>-
Introduction
In recent years, the concept of the Internet of Things (IoT) is gaining momentum due to the development of the wireless networking technologies, such as Long Term Evolution Advanced (LTE-A), Wireless Fidelity (WiFi), Bluetooth, ZigBee, and so forth. Conventionally, these network technologies are utilized for establishing communication from the Person to Person (P2P) or the Person to Machine (P2M) perspectives. However, due to the diversification of the network equipment, Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communication is also utilized in numerous circumstances, such as inside homes, commercial buildings, schools, hospitals, and factories. The development of smaller and less expensive wireless devices enables not only smart-phones, tablets, and personal computers but also cars, home electrical appliances, and so forth, in order to connect them to the Internet. For example, electric lights, air conditioners, and water heaters can be connected to the network inside a building, and thus, they may be controlled for optimizing the environment inside the building with minimum power.
-
Classifications and Examples of IoT Systems
As a result of rapid development in communication technologies, a huge variety of networking technologies with different scales are being utilized in our daily life. Due to the large diversity of networks being deployed, the concept of IoT can be broadly classified in terms of network scale as illustrated in Fig. 1. In this section, we aim to classify IoT systems and introduce examples of different IoT systems according to their respective scales of the network.
2.1 Internet of Nano Things Firstly, we introduce the concept of the Internet of Nano Things (IoNT) as a type of IoT with small networks comprising extremely small devices in personal area. In the IoNT, by embedding nano-sensors to the various objects and devices that surround users, it becomes possible to add a new dimension to the IoT. Such miniature sensors, interconnected through nano-networks, could provide data from the things (i.e., devices) deployed in hard-to-access areas. The IoNT is expected to lead to the discovery of novel insights and applications in the IoT field.
2.2 Internet of WiFi-Enabled Things Secondly, we show the concept of IoT consisting of WiFienabled devices in middle size of networks. WiFi has nowadays become a popular means of wirelessly connecting various electronic devices to the Internet. Recently, not only mobile devices such as smartphones and laptops but also home appliances and various kinds of sensors in local area are connected to the Internet by employing WiFi. Using the WiFi technologies, along with the concept of D2D, is considered to provide more flexible IoT systems. In the work [3], Tozlu et al. focus on IoT constructed by WiFi equipped sensors and actuators. Especially, they focus on energy consumption of devices in the network. Since various types of devices are connected to the same network in this considered IoT, the difference in energy utilization becomes a significant problem to guarantee network connectivity. In their work, the devices having WiFi functionality are categorized into three types: AC-powered devices (home appliances, PCs), rechargeable devices (laptops, smart-phones), and battery-powered devices (sensors like smoke detectors, motion detectors, and so forth).
3.IoT adoption barriers
-Lack of interoperability and unclear value propositions:
Despite a shared belief in the potential of the IoT, industry leaders and consumers are facing barriers to adopt IoT technology more widely. Mike Farley argued in Forbes that while IoT solutions appeal to early adopters, they either lack interoperability or a clear use case for end-users.A study by Ericsson regarding the adoption of IoT among Danish companies suggests that many struggle “to pinpoint exactly where the value of IoT lies for them”.
4.Privacy and security concerns:
As for IoT, information about a user’s daily routine is collected so that the “things” around the user can cooperate to provide better services that fulfill personal preference.When the collected information which describes a user in detail travels through multiple hops in a network, due to a diverse integration of services, devices and network, the information stored on a device is vulnerable to privacy violation by compromising nodes existing in an IoT network.
For example, on 21 October 2016, a multiple distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks systems operated by domain name system provider Dyn, which caused the inaccessibility of several websites, such as GitHub, Twitter, and others. This attack is executed through a botnet consisting of a large number of IoT devices including IP cameras, gateways, and even baby monitors.
Fundamentally there are 4 security objectives that the IOT system requires:
- data confidentiality: unauthorized parties cannot have access to the transmitted and stored data.
- data integrity: intentional and unintentional corruption of transmitted and stored data must be detected.
- non-repudiation: the sender cannot deny having sent a given message.
- data availability: the transmitted and stored data should be available to authorized parties even with the denial-of-service (DOS) attacks.

Traditional governance structure
A study issued by Ericsson regarding the adoption of Internet of things among Danish companies identified a “clash between IoT and companies’ traditional governance structures, as IoT still presents both uncertainties and a lack of historical precedence.”Among the respondents interviewed, 60 percent stated that they “do not believe they have the organizational capabilities, and three of four do not believe they have the processes needed, to capture the IoT opportunity.”This has led to a need to understand organizational culture in order to facilitate organizational design processes and to test new innovation management practices. A lack of digital leadership in the age of digital transformation has also stifled innovation and IoT adoption to a degree that many companies, in the face of uncertainty, “were waiting for the market dynamics to play out”,further action in regards to IoT “was pending competitor moves, customer pull, or regulatory requirements.”Some of these companies risk being ‘kodaked’ — “Kodak was a market leader until digital disruption eclipsed film photography with digital photos” — failing to “see the disruptive forces affecting their industry” and “to truly embrace the new business models the disruptive change opens up.” Scott Anthony has written in Harvard Business Review that Kodak “created a digital camera, invested in the technology, and even understood that photos would be shared online”[244] but ultimately failed to realize that “online photo sharing was the new business, not just a way to expand the printing business.”
In 2025
- It is estimated that there will be more than to 21 billion IoT devices,A quick look back shows where IoT devices are going. Consider: In 2016, there were more than 4.7 billion things connected to the internet, according to IOT Analytics. Fast-forward to 2021? The market will increase to nearly 11.6 billion IoT devices.
-
More cities will become “smart”:
Consumers won’t be the only ones using IoT devices. Cities and companies will increasingly adopt smart technologies to save time and money.
That means cities will be able to automate, remotely manage, and collect data through things like visitor kiosks, video camera surveillance systems, bike rental stations, and taxis.
-
Artificial intelligence will continue to become a bigger thing
Smart home hubs, thermostats, lighting systems, and even coffee makers collect data on your habits and patterns of usage. When you set up voice-controlled devices, you allow them to record what you say to them and store those recordings in the cloud. In most cases, the data is collected to help facilitate what is called machine learning.
Machine learning is a type of artificial intelligence that helps computers “learn” without someone having to program them. The computers are programmed in a way that focuses on data that they receive. This new data can then help the machine “learn” what your preferences are and adjust itself accordingly. For instance, when a video website suggests a movie you might like, it’s likely learned your preferences based on your past choices.

-
Routers will continue to become more secure and smarter
Because most consumer IoT devices reside in the home and can’t have security software installed on them, they can be vulnerable to attacks. Why? A lot of manufacturers work to get their IoT products to market quickly, so security may be an afterthought. This is where the home router plays a very important role. The router is essentially the entry point of the internet into your home.
While many of your connected devices cannot be protected, the router has the ability to provide protection at the entry point. A conventional router provides some security, such as password protection, firewalls, and the ability to configure them to only allow certain devices on your network.
Router makers will likely continue to seek new ways to boost security.
-
6. 5G Networks
Major wireless carriers will continue to roll out 5G networks. 5G — fifth-generation cellular wireless — promises greater speed and the ability connect more smart devices at the same time.
Faster networks mean the data accumulated by your smart devices will be gathered, analyzed and managed to a higher degree. That will fuel innovation at companies that make IoT devices and boost consumer demand for new products.
]]>Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property WINP_SnippetShortcodePhp::$plugin is deprecated in /home3/miningio/public_html/S5SYSTEM/wp-content/plugins/insert-php/libs/factory/shortcodes/shortcode.class.php on line 95
The Internet of Things (IoT) has quickly emerged as a strategic transformation agent for all industries as it blends the physical and digital worlds. By connecting things and providing “smartness” to them, new value is created across a number of sectors in the Networked Society.
Ericsson’s latest Mobility Report predicts that we are heading for an IoT-dominated world by the end of 2018. That’s less than two years from now! So for the first time ever, the mobile phone will no longer be the most common and most intimate device we will use to get ourselves connected to the Internet — it will be our wearables, cars, home appliances, cities, industries, you name it! And in five years, we expect 28 billion connected devices around the world, with more than half being IoT devices.
As things are connected, new opportunities arise for service providers, industries, cities and enterprises whereby new solutions are developed that change the world we live in and the way we interact with it. Let me give you a couple of real-life IoT examples that are enabling this change.

Connected city: Reducing crime in Brazil
São Jose Dos Campos City was suffering from an increased crime rate, so city administrators decided that one way to combat this situation was through technology. Ericsson helped the city become safer by modernizing the existing city public safety, emergency response and traffic management operations with a new Emergency Response & Traffic Management Control solution. Starting with the integration of existing CCTV and traffic light infrastructure, 500 new video cameras, a new fiber network infrastructure and 100 new tablets in vehicles were added.
In true IoT fashion, these systems are integrated with real-time GIS information, vehicle tracking, traffic information systems and multi-agency integration with real-time tracking and dispatch of Police and Traffic department vehicles. This modernization project generated tangible and live-saving results, as the homicide rate was reduced by 18% while also improving the availability of evidence needed to successfully prosecute criminals.
Connected Water: Keeping our water supply safe
Ensuring “safe” water sources for human consumption is key to any community but the current monitoring solutions are complex, with several components required to solve the problems of power, telemetry and maintenance. They are expensive, with a focus on high-precision measurements instead of environmental fingerprinting. Monitoring is not real-time, so the ability to alarm, alert, and share information among stakeholders is limited.
In Georgia, we are working with the Connected Water solution for the Chattahoochee River, where low-cost sensors are now reporting water quality via cellular networks, turning a reactive monitoring process into a prescription- and prevention-based process that significantly reduces the cost of monitoring and will exponentially decrease the cost of treatment over time through real-time early identification of abnormal conditions in the water.
This IoT innovation, which delivers strong sustainability benefits, has just won the CTIA Super Mobility’s Annual Emergency Technology Award.
Connected Buildings: Improving efficiency, utilization and convenience
Another innovative IoT solution area is around smart buildings, where our technology assists facility managers in space management, space utilization, planning of maintenance based on usage, control of temperature, air quality, humidity and ventilation optimization.
In one instance, data from sensors allows facility managers to take actions to adjust the temperature profiles where each degree adjustment can reduce heating/cooling cost by 5%. In another case, our IoT solution allows building managers to do meal planning and preparations to match the number of people in the buildings, thus reducing food wastage: Find out more in the following video:
Now, let’s shift gear towards the consumer market. Our recent ConsumerLab study reveals that wearable devices related to personal safety and security were rated highly by smartphone users, with ideas such as panic buttons and wearable location trackers being the most popular.
That study also reveals that the feeling of safety drops by 20% among consumers from day to night. Women in particular feel vulnerable in situations such as waiting for public transport at night. And while smartphones do lend a sense of safety, with security-related apps, consumers desire a discreet way to send an alert for help. So security wearables will be one major area IoT can add significant value to consumers.

A new generation of network technologies for IoT
Whether in the enterprise or consumer context, IoT starts with connectivity. There are already more than 400 million cellular IoT devices, but that is just the beginning. A wide range of new technologies are emerging that enable new value and capabilities for connecting the next new “thing” to a new generation of analytics and applications.
A new wave of connectivity innovations in LTE, LPWA and the emergence of 5G are bringing new capabilities and cost/performance options tailored to specific devices and applications. These technologies bring new capabilities to bear while significantly lowering cost to bring the next thing “online.”
To ensure success, service providers must get connectivity right early in the game so they can build a successful IoT business on top of it. The “Massive IoT” market is a growth area dominated by low-cost, low-bandwidth sensor-based devices. This segment is served by a new generation of highly cost efficient GSM and LTE cellular technologies known as Category M1 and NB-IoT, whereby the trusted and secure GSM and LTE connections of today are expanded for use by millions of potential IoT applications.
In my 5G blog published on Light Reading, I talked about the emergence of 5G and how it is bringing a new set of technologies that enable high-bandwidth, low-latency real-time IoT applications. This will be fundamental to the “Critical IoT” market, for example, enabling an autonomous car to be able to apply its brakes in a couple of centimeters instead of a couple of meters.
When considering which technology to pick for any IoT implementation, there are pros and cons of capability, security, cost and longevity of the solutions that must all be taken into account: Bridging that new connection to a new generation of cloud and analytics technologies that drive advanced business and operational transformation is key to harnessing the full potential of IoT.
With connectivity as a foundation, communications service providers are in a prime position to benefit from the IoT evolution and they will need a long-term vision to evolve their networks while having a clear view of where else to position themselves along the value chain to capture future IoT market opportunities.
The IoT ecosystem is still nascent, fragmented and complex, with myriad established as well as emerging players from all quarters of the ICT landscape. For service providers and enterprises alike, it’s essential to have an IoT transformation partner that can help them navigate the complexity, that can bring not only connectivity technology, but also platforms and components such as analytics and monetization, and expertise in vertical industries — with an active ecosystem role. They need a partner they can trust and work with, whatever their IoT aspirations.
]]>Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property WINP_SnippetShortcodePhp::$plugin is deprecated in /home3/miningio/public_html/S5SYSTEM/wp-content/plugins/insert-php/libs/factory/shortcodes/shortcode.class.php on line 95
Deprecated: Creation of dynamic property WINP_SnippetShortcodePhp::$plugin is deprecated in /home3/miningio/public_html/S5SYSTEM/wp-content/plugins/insert-php/libs/factory/shortcodes/shortcode.class.php on line 95
If you have not been living under a rock, you must have heard about the Internet of Things or IoT. IoT applications are ruling the digital world all around and revolutionizing the computing capabilities and data collection and analytical technology.
Best Machine Learning Courses & AI Courses Online
Now, the first question that you might have is: What is IoT or the Internet of Things? IoT is a platform where many embedded devices are connected with one another through the internet. These devices collect and exchange data with one another. Due to the collection of relevant data, IoT is able to interact and learn from one another, similar to human beings.
It is the active use of IoT which can actually make a city ‘smart’. IoT work with the help of predictive analysis and machine learning and the combination of both can boost the efficiency of specific work areas easily. There are many IoT applications and it continues to increase.

Top 9 IoT Real World Applications
-
Agriculture and Pest Control
Since we are going to look into the different IoT applications and the various IoT use cases, let’s start off with the areas where IoT use is most overlooked – farming. Agriculture is essential for human survival and the way the population keeps multiplying, it can be hard to maintain such large-scale agriculture without a major revolution
Integrating IoT applications with farming can help to boost the production and keep it in line with the population explosion happening all over the globe. IoT applications can result in precision farming – that is, use of analytical data to understand soil moisture level, climatic changes, plant requirement, etc, and thus boost yield as well as encourage efficient use of resources.
This method can also be used for livestock management as well. A threat that the agricultural sector has always faced is pest infiltration. However, in one of the recent IoT use cases, a company, Semios, makes use of sensors to track pest population. There are other IoT systems as well which could be used to trap pests and notify authorities about it.
-
Environment
In recent times, we are becoming more and more aware of the environment and the damage that human activities have caused. Now, we are slowly trying to correct our mistakes and tackle environmental issues. We can make use of IoT applications to help us with this goal.
Some of the areas where IoT are working is preservation of bees. Honey Bees are facing a threat in this polluted world. Climate change is affecting them as well. However, by implanting IoT devices, beekeepers can take better charge of preserving hives. Using IoT with connected sensors, it is possible to keep track of the hive temperature, amount of food present in the hives and also, the pollen collection. IoT can be also used in waste management also, helping us take better care of our environment.
-
Smart Home Applications
Smart homes are probably the most common of all IoT use cases. The concept of smart homes has revolved around the internet for a long time. When Mark Zuckerberg displayed his smart home Jarvis, many people felt that they could actually fulfill their dream of having a Smart home.
A smart home works with the active use of IoT applications. Smart home devices collect and share information with one another in an integrated platform and automate their actions based on the owner’s preference. Hence, it is clear that they engage in a learning process to understand the preferences of their owner.
There are many IoT use cases related to Smart home appliances, but one of them can be Smart Thermostats, which monitor and control home temperatures to the comfort of the owner. Plus, there is smart lighting as well where the lighting adjusts themselves based on the user preference as well as external lighting.
-
Health Care
The use of IoT in the healthcare sector can redefine healthcare as a whole. The entire healthcare sector comprises physicians, patients, hospitals, and health insurance companies. IoT can target and enrich each of these parties. Patients already have access to several forms of wearables like fitness bands and blood pressure monitors to help with their health.
There are also alert mechanisms put in these devices to notify doctors or family members in the case of emergencies. For physicians, it is quite easy to get into the history of a patient through the IoT device and access real-time health data easily. Real-time health data can also be used to increase the efficiency of clinical trials. IoT devices can be used inside hospitals to track locations of medical devices like defibrillators or wheelchairs and also help with inventory management, monitoring the environment, and temperature regulation. Learn more about machine learning applications in healthcare industry.
Since most IoT devices collect data and store them in the cloud, health insurance companies can access this data to track the routine activities of a patient (their lifestyle choices), whether they are adhering to their treatment plans, or even looking into the operation processes.

-
Smart Cities
Many governments plan to build smart cities – that is – cities which heavily use IoT for several reasons like traffic management, public transportation, parking, utility billing, etc. Smart Cities can be referred to as large-scale IoT applications which cover a lot of problematic areas in a city.
While costly, it can be safe to say the benefits far outweigh the cost. With the combination of sensors, GPS data collection, and cloud platforms, it will be easy to monitor traffic conditions of a specific area, plan construction programs by predicting their impact on traffic and find alternative routes when necessary.
Use of smart billing for household use of energy and smart street lighting can help in the management of energy use. Another use case of the many IoT use cases is improving public safety by using smart cameras or smart microphones to help detect crime in any area across a city.
-
Safe Driving
With the increasing use of mobile phones, there has been a tragic rise in car accidents. These accidents have been connected to distracted driving. While there have been warnings against the use of mobile phones while driving, many drivers do not pay heed to it. However, with the help of IoT technology, it is possible to track the mobile usage of drivers during driving and block distracting apps.
IoT applications can also be used to understand driver behaviour and coach drivers based on how they are driving. A recent area where IoT is being used is in the construction of driverless cars. While it seems like something from the future, driverless cars are already in the making. These cars use advanced sensors and gyroscopes, all of which are connected to cloud platforms and the internet.
Using this platform, the driverless car is able to data from a variety of sources which tells them about the traffic conditions as well as potholes, sharp turns, speed breakers and other useful information required for driving. Driverless cars can be a perfect addition in a Smart City to ensure smooth traffic conditions.
-
Waste Management
We are slowly moving into a world which takes waste creation seriously. While many companies are moving away from non-biodegradable goods, it is important to manage the waste already being generated. IoT can bring a lot on the table to help with waste management.
One of the IoT use cases is selecting the right route for garbage trucks. IoT applications can notify truck drivers about filled dustbins and set a route for them so that they do not have to waste time by exploring locations with empty dustbins. IoT devices can also help in developing Smart bins, that is, trash bins which can segregate waste into categories like plastic, metal, glass or paper. Bin-e, a Polish company, has already generated Smart Waste Bins as one of the many IoT use cases related to waste management.
-
Tackling Industrial Issues
Using IoT in the industrial sector is sometimes seen to be similar to the Industrial revolution. How can IoT help with Industries? In the manufacturing department, IoT can be used in asset management and inventory management. Implanting IoT in the manufacturing sector can help in tracking the efficiency of the systems being used, detect any errors in the machinery, detect causes of lack of efficiency, etc. IoT in the industry can help in tackling unplanned downtime too.

-
Supply Chain
If you are using Amazon or Swiggy, you might be aware of the tracking system they use to track the delivery of your goods. Supply chains have been using IoT applications for quite some time. It has helped suppliers to track goods in transit as well as get immediate customer feedback with the help of a rating system. IoT systems can also help the supplier or drivers to preserve the goods better during transit by communicating information about temperature and pressure that the item is being preserved in. Hence, IoT can optimize workflow by improving the supply chain transit.
Popular Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Blogs
Wrapping Up
IoT is a game-changing technology that is affecting many different industries. More and more companies and civic bodies are taking up IoT applications. The world is slowly transforming into a ‘Smart’ world with Smart solutions. IoT has given both businesses and governments many options to improve their work and become more efficient. Plus, for IoT professionals, a bright future shines on the horizon with brand new opportunities coming up in the near ‘Smart’ future.
If you are curious to master Machine learning and AI, boost your career with an Advanced Course on Machine Learning and AI with IIIT-B & Liverpool John Moores University.
]]>