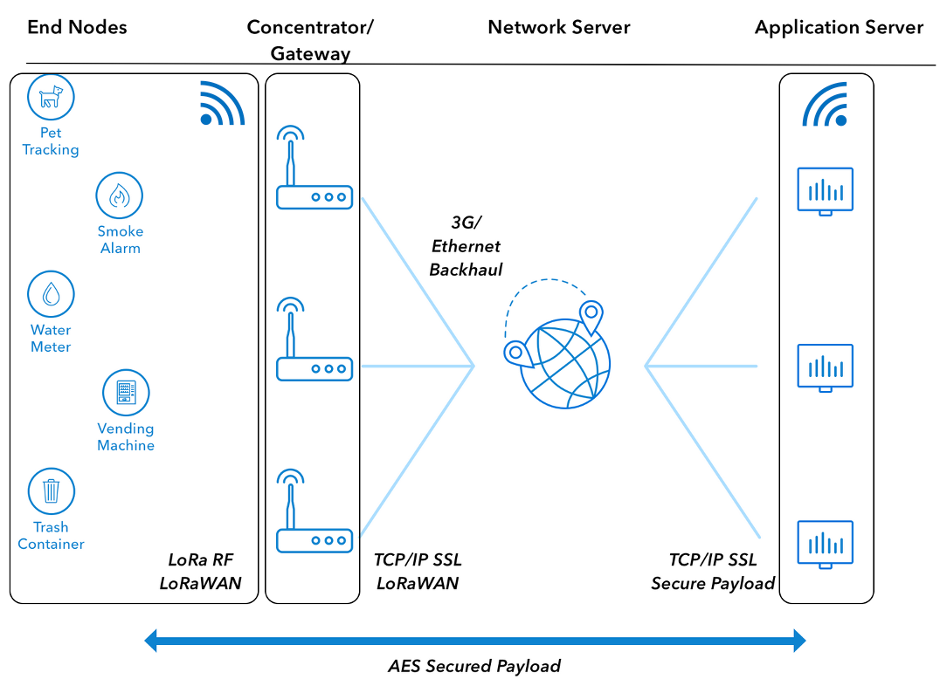
The Long-Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN) media access control (MAC) protocol is a global standard that offers a long-range bi-directional transmission and reception of signals for communication of up to 15km. It is designed for long range wireless applications and internet connected applications. It uses very little power compared to other communication protocols and technologies. Given its low power consumption, a device utilizing LoRaWAN can last up to 10 years on a single battery. This makes it applicable to IoT solutions and is widely practiced in the industry.

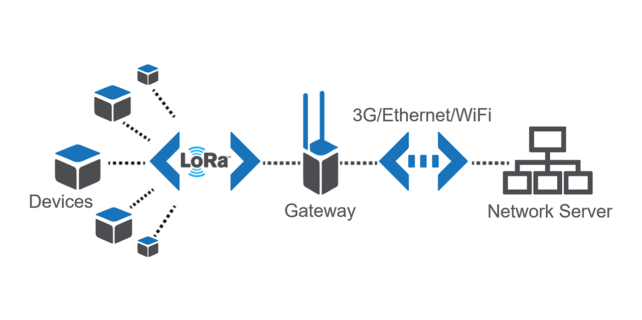
Now, going deeper into LoRaWAN, let’s start by first understanding LoRa. LoRa is complementary to existing IoT communication technologies. It utilized a very narrow Bandwidth which is used for small data transmission. Also, LoRa is very robust to interference. Another aspect of LoRa is its multi-path and fading resistance and doppler shift resistance. This is because LoRa transmits low data rate with high spreading factors. It is designed for IoT applications given its long range of data transmission capability. However, longer range of coverage and low power consumption come with a cost, and that is bandwidth. Therefore, LoRa is primarily used for applications where connected devices are asleep most of the time and when they are required to read and send data, they wake up for a short period of time and then go back to sleep.
Now, LoRaWAN is a communication protocol used on top of LoRa to provide the 3 pillars of security. These are Authenticity, Confidentiality and Integrity. LoRaWAN provides security on 2 different levels. First is the network layer which uses a network session key (NwkSKey) which is responsible for integrity and authenticity. Secondly, we have the application layer where the security is provided by the application session key (AppSkey) which is responsible for the confidentiality.
Advantage:

- Ultra-Low Power
- Long Range
- Deep Indoor Penetration
- License Free Spectrum
- Geolocation
- Public and Private Deployments
- End-to-End Security
- Firmware Updates over the Air
- A very Large Ecosystem
LoRaWAN Applications:

- Smart Farming (water, air, soil quality analysis & Control)
- Smart Cities, Homes, Buildings, Offices
- Supply Chain Logistics, Asset Tracking
- Smart Energy Monitoring (Water, Gas, Electricity)
- Smart Parking
- Water / Gas / Electricity Leakage
- Liquid Level monitoring (Water and Fuel tanks)
- Structural Health
- Machinery Management
- Access Management
Optimization points for LoRaWAN implementation:
Devices must always comply to LoRaWAN specifications.
Reduce the frequency of transmitting messages to minimum..
Shorter messages can lead to longer battery life and therefore more capacity.
Implement forward error correction to account for packet loss.
Add random jitter to message sending intervals so there is no congestion in the network.
Use adaptive data rate mechanism for stationary devices.
LoRaWAN Architecture: